Your complete guide
Histamine Intolerance Top FAQs
Are you suffering from Histamine Intolerance?
What is Histamine Intolerance?
You may feel confused about what histamine intolerance is or how to address it.
Histamine intolerance is a condition that affects around 1% of the population[1]. While that might seem small, the symptoms can feel overwhelming. You don’t need to feel confused anymore!
This site will answer all of your questions about histamine intolerance, including:
- What are the signs of histamine intolerance?
- How does DAO affect histamines?
- Will antihistamines cure histamine intolerance?
- What foods worsen histamine intolerance?
- What is a low-histamine diet?
- Can you still eat citrus fruits if you have histamine intolerance?
- Is histamine intolerance an allergic reaction?
- Are there supplements that can help histamine intolerance?
- What are the best histamine intolerance probiotics?
And so much more!
The FAQs below will answer your top questions.
What is
Histamine
and DAO?
What Are the Symptoms of Histamine Intolerance?
Histamine intolerance may cause different responses in different people.
Common Signs
Some common signs that you might experience if you get too much histamine from foods include:
- Digestive discomfort, like bloating and abdominal pain
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Dizziness or headaches
- Sneezing or runny nose
- Hives (urticaria)
Severe Cases
In severe cases of histamine intolerance responses, you may also experience[2]:
- High blood pressure
- Arrhythmia
- Other gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal pain
High Risk
People who already have certain medical conditions may be at higher risk for histamine intolerance. These may include the following:
- IBD or Crohn’s disease
- IBS
- Eczema
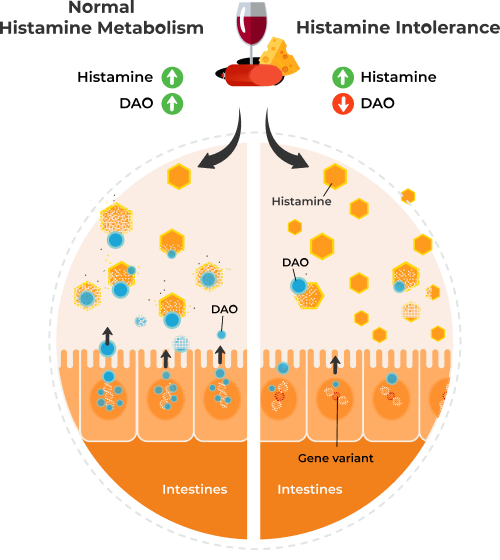
What is DAO?
DAO is short for diamine oxidase. DAO is a gene that produces an enzyme of the same name.
Your body makes the DAO enzyme in the intestinal tract, the kidneys, and the thymus. It breaks down histamine in the body. Histamine is a natural compound that you get from food and that your body makes in response to environmental triggers, like seasonal allergens. It also helps to manage some functions in certain body systems, including:
- The Digestive System
- The Immune System
- The Nervous System
When your DAO gene has certain variants, or you eat a lot of dietary histamines, your body may not be able to make enough DAO enzyme to break it all down. You may experience effects of excess histamine, which can include:
- Digestive discomfort
- Diarrhea and constipation
- Headaches or dizziness
- Nasal congestion
- Sneezing
- Itching
How Does DAO Affect Histamines?
The DAO enzyme helps the body break down and remove excess histamine from the body.† Your levels of histamine depend on your body’s ability to make DAO.
Histamine is a biogenic amine—a type of compound that helps to regulate many metabolic and physiological functions in the body.
They are needed to help promote normal[3]:
Movement
Behavior
Emotions
Blood Pressure
Body Temperature
Hormone Production
When you do not have enough DAO enzyme, one or more of these body systems may be affected if you eat or drink large amounts of histamine-containing foods.
Supplements that contain the DAO enzyme can help the body process excess histamine[4]. This can help support a healthy histamine response.†*
Histamine
Intolerance
What Deficiency Causes Histamine Intolerance?
Not having enough DAO enzyme may lead to a histamine intolerance response.
DAO activity can be affected by many things, including[5]:
- Genetic variants
- Alcohol use
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
- Some medications
- Eating a lot of histamine-containing foods
Histamine Receptors
Histamine receptors direct cellular responses to histamine.
They are located throughout the body and are found in:
- The Heart and Vascular System
- The Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Lungs
- Immune Cells
- Smooth Muscle in the Intestinal System
- Adrenal Glands
Histamine Responses
Histamine responses are also affected by certain nutrients.
Up to 20% of people may take medications or nutritional supplements that may decrease the enzymatic activity of DAO. Nutrients that may have an inhibitory effect on the DAO enzyme may include[6]:
- Chloroquine: 90% DAO Inhibition
- Verapamil: 50% DAO Inhibition
- NAC: 20% DAO inhibition
What Happens When You Have Too Much Histamine In Your Body?
Mast cells are a type of immune cell known as white blood cells.
Mast cells are found in all types of connective tissue, such as:
- Under The Skin
- Around Lymph Vessels
- Near Blood Vessels
- In The Intestines
- In Nerves
- In The Lungs
Mast cells influence how the immune system responds to certain things, including bacteria and infections. Mast cells contain histamine and other chemicals that they release in response to triggers.
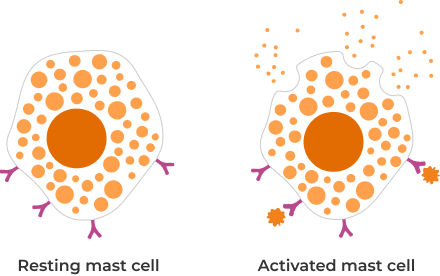

Too much histamine for your body to process results in symptoms like itching, sneezing, hives, and digestive discomfort. In extreme cases, it can result in breathing problems. This does not occur from food-derived histamine intolerance, but may happen with IgE food allergies or mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS). MCAS does involve the excess release of histamine, but many other chemicals are produced by mast cells, too.
DAO levels can affect how well your body breaks down food-derived histamine from non-allergic reactions.†
HNMT
You may also struggle to break down histamine if you have variants in another gene known as HNMT.
Histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT) is an enzyme made by a gene of the same name[7]. This enzyme has a large presence in the central nervous system (CNS)[8]. It breaks down histamine and functions as a neurotransmitter. A variant in the gene could make it harder to break down or metabolize histamine.
It is possible to have gene variants in both DAO and HNMT.
When you have too much histamine for your body to process, you are more likely to experience one or more histamine intolerance responses, such as itching, sneezing, hives, or rashes.
What is the Root Cause of Histamine Intolerance?
There is no single root cause of histamine intolerance.
Factors that may contribute to histamine intolerance include:
- Leaky gut syndrome
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
- Mutation in the DAO gene
- Mutation in the HNMT gene
- Excessive dietary intake of histamine foods
- Low magnesium intake
- Regular alcohol intake
If you have histamine intolerance, relief is possible. But first, you have to know if histamine intolerance could be affecting you.

How Do You Test for Histamine Intolerance?
Unfortunately, there are no definitive diagnostic tests for histamine intolerance.
Healthcare providers can test DAO enzyme activity and histamine levels via lab work. The results are not validated for the diagnosis or treatment of histamine intolerance since they do not always compare to symptoms.
A healthcare provider may diagnose you with histamine intolerance after ruling out the possibility of food allergies or MCAS.
Will Antihistamines Cure Histamine Intolerance?
Antihistamines can block histamine activity, but they do not cure the root cause of histamine intolerance.
Genetics
If you have a DAO or HNMT genetic variant, taking antihistamines will not make your genes work optimally.
Food Sensitivities
If you have food sensitivities, antihistamines only handle the histamine-related response, but will not prevent a histamine reaction the next time you eat it.
Histamine intolerance cannot be cured. Symptoms can be managed with a combination of dietary changes, lifestyle management, DAO enzyme supplementation, and/or antihistamines.†*
Histamines
& Diet
What is a Low-Histamine Diet?
What diet is best for histamine intolerance?
The answer depends on your symptoms and personal sensitivity.
Reminder:
A low-histamine diet is not appropriate for addressing histamine responses that
occur because of immune-driven food allergies.
You likely don’t need a histamine-free diet, which would be difficult since small amounts of histamines are found in many common foods.
If you find that you frequently experience symptoms of histamine intolerance, a low-histamine anti-inflammatory diet can make a big difference.
There are a few ways that you can approach a low-histamine diet.
Elimination Diet
This is where you do a trial period of eliminating all high-histamine foods.
After a period of time, usually a few days or a week, you add one histamine-containing food back to your diet. You then track whether you have histamine intolerance symptoms based on eating that food. If you do, you may be sensitive to that particular food and may need to avoid it longer. If you don’t, it is likely the histamine in that food is not a problem for you.
However, some people can always handle one histamine-rich food at a time. It is usually the histamine load that can lead to signs of histamine intolerance. Many people may consume a high-histamine diet without even knowing it. A histamine elimination diet can help you realize which foods have a lot of histamine so you can create better balance in your food intake.
Avoid High-Histamine Foods
You aren’t getting histamine intolerance symptoms from foods you never eat.
Instead, take a look at your diet and consider foods that you eat every day or many times per week. Do any of them fall on the high-histamine list? Cutting back could help you alleviate symptoms of histamine intolerance.
Foods that are generally low in histamines include:
Fresh meats and poultry
Leftovers, reheated, cured, or processed foods contain more histamines
Fresh fruits
Fresh fruits like blueberries, apples, peaches, mango, and apricots
Fresh Vegetables
Fresh vegetables like onion, asparagus, broccoli, cucumbers, beets, and sweet potatoes
Gluten-Free Starches
Gluten-free starches like potatoes, rice, and oats
Dairy Products
Dairy products like butter and milk
What Foods Worsen Histamine Intolerance?
High-histamine foods worsen histamine intolerance.
These can include:
- Fermented foods like soy and sauerkraut
- Red wine and alcohol
- Salami
- Tuna canned
- Fish Sauce
- Eggplant
- Fermented foods like soy and sauerkraut
- Aged Cheeses Like Feta and blue cheese
- Red wine and alcohol
- Salami
- Mackerel
- Tuna canned
- Fish Sauce
- Dry cured pork belly
- Spinach
- Eggplant
- Additives of all kinds
- Preservatives of all kinds
- Aged Cheeses Like Feta and blue cheese
- Mackerel
- Dry cured pork belly
- Spinach
- Additives of all kinds
- Preservatives of all kinds
Histamine-rich foods, histamine liberators, and foods with antinutrients can all lead to the release of histamine.
The amount of histamine that you can tolerate without symptoms depends on many factors. Some people are more sensitive than others.
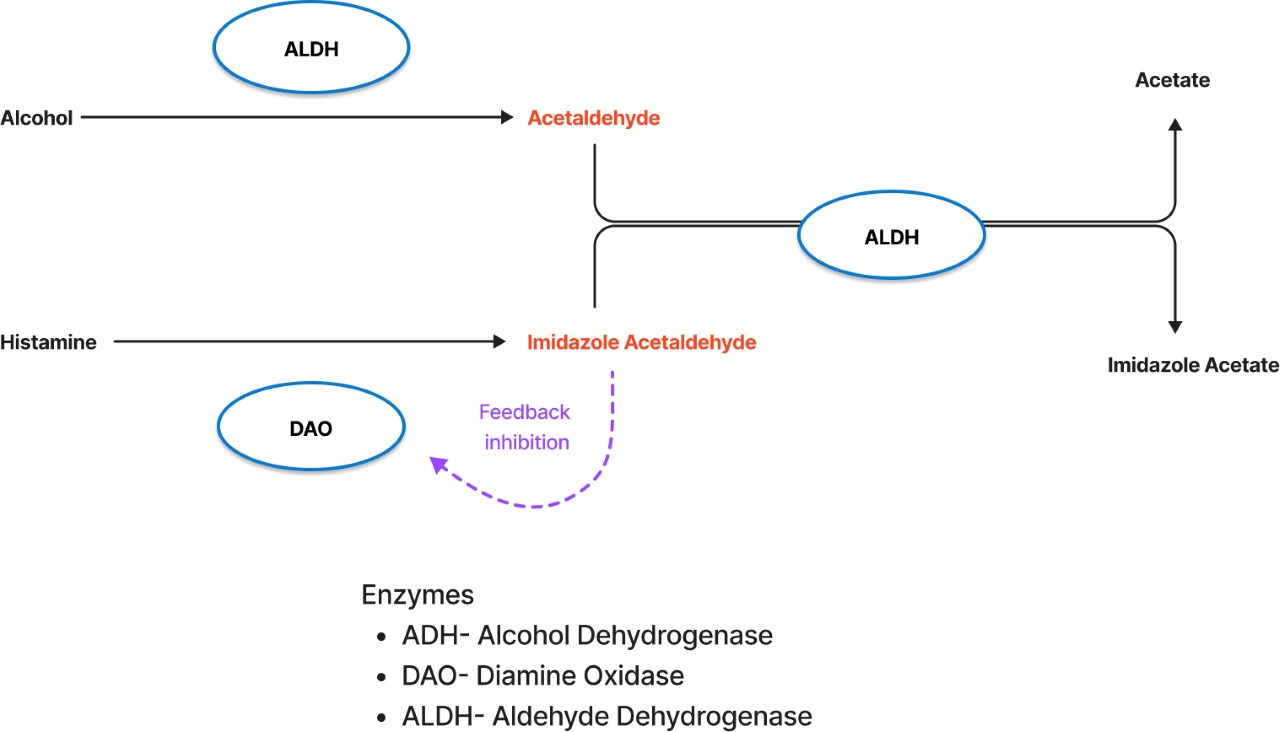
Alcohol inhibits DAO
When alcohol is broken down in the body, aldehydes are produced. A build up of aldehydes will shut down the activity of DAO. Therefore, alcohol has two strikes against it.
- Alcohol is high in histamine
- Alcohol can slow down DAO activity

Can You Still Eat Citrus Fruits If You Have Histamine Intolerance?
Citrus fruits might trigger histamine intolerance responses.
While you may not have to avoid all of them, many healthcare practitioners recommend limiting or avoiding citrus fruits if histamine intolerance effects are severe.
Alternatively, it may help to take DAO enzyme when consuming high-histamine or histamine-releasing foods.†*
Is Histamine Intolerance an Allergic Reaction?
Food allergies are different from a histamine intolerance response, although both involve histamines[9].
Food Allergies
A food allergy is a serious reaction driven by the immune system in response to ingested allergens. Histamines are released from mast cell stores to respond, causing the signs and symptoms of an allergic reaction.
You can get allergy tests to distinguish your responses to certain foods. These typically involve skin-prick tests or lab work.
Food-derived Histamine and Histamine Intolerance
Food-derived histamine and histamine intolerance is triggered by non-allergic food hypersensitivity. Food intolerances, like histamine intolerance, are not IgE allergic reactions[10]. However, people who have IgE allergies may also have histamine intolerance.
You can use an elimination diet to help pinpoint foods that worsen a histamine intolerance reaction.
Histamine Intolerance
Support Supplements
What Supplements Support a Healthy Histamine Response?†
Some supplements can help support how your body responds to histamine that comes from foods.†
They may be a good support to a histamine intolerance protocol, like a low-histamine diet.†
Supplements to help support those experiencing histamine intolerance include:†
- Probiotic strains that are not known to produce histamine in the gut, including bifidobacterium infantis, bifidobacterium longum, and lactobacillus plantarum
- Herbal and plant-based compounds that support the body’s healthy inflammatory response, such as stinging nettle, quercetin, and bromelain
- DAO enzyme*
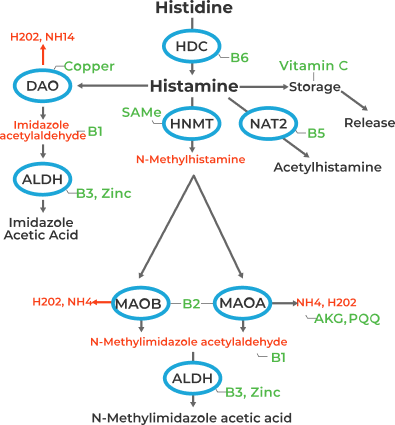
- Cofactors that help the HNMT and DAO genes function optimally, including copper, zinc, and vitamin B6 (See Histamine Pathway below).
Histamine Pathway



What Are the Best Histamine Intolerance Probiotic Strains?†
Some strains of probiotics actually produce histamine in the gut.
If you already have histamine intolerance issues, you don’t want to add even more to your gastrointestinal system!
The good news is that there are probiotic strains that are not known to increase histamine production.
These probiotics strains include:
- Bifidobacterium infantis
- Bifidobacterium bifidum
- Bifidobacterium longum
- Bifidobacterium lactis
- Bifidobacterium breve
- Lactobacillus salivarius
- Lactobacillus plantarum
How Can I Lower My Histamine Levels Quickly?
The build-up of histamine is uncomfortable.
It’s natural to wonder how you can quickly resolve the symptoms of histamine intolerance when they start. The best ways to help support food-derived histamine intolerance symptoms once they’ve started is to:†
- Take DAO digestive enzyme – to support a healthy metabolic response to digested histamine†*
- Consider an over-the-counter antihistamine – to block histamine activity for short term relief
These options may not be appropriate for everyone. Talk to your health professional before adding any new supplements or medications to your regimen.
Solutions
How Do You Fix Histamine Intolerance?
Histamine intolerance is like other food sensitivities.
You may experience it more strongly for a season or it may be a recurring issue that you need to manage.
The best way to address histamine intolerance is to understand what triggers a response in you. Then you can manage your triggers in a variety of ways, such as:
- Following a low-histamine diet
- Avoiding high-histamine or histamine-liberating foods
- Using DAO enzyme supplements when you eat high-histamine foods†*
- Using other supportive nutrients†
There is no one right way to address histamine intolerance.
Your individual response and triggers may be different from someone else’s. But with DAO enzyme support, you may still be able to enjoy your favorite histamine foods.†
4 Steps to Take
We hope this information has been helpful for you.
While it cannot replace the advice from your qualified healthcare provider, there are easy steps you can take to start feeling better today. If you think you might be suffering from Histamine Intolerance, our team of experts recommends taking the following steps.
Always check in with your healthcare provider before starting any new health protocol!
1.
Conduct an elimination diet.
This is the gold standard for identifying Histamine Intolerance. Follow a low histamine diet for 4 weeks. Then, slowly re-introduce one high-histamine food at a time and look for symptoms. Keep a diet/symptom log. This will help you easily identify high-histamine foods you are reacting to.
2.
Consider a DAO supplement.
Many people find relief by supplementing with the DAO enzyme before meals. DAO is the main enzyme that breaks down histamine in your gut. While your body makes this enzyme, it’s also available in supplement form.†*
3.
Support ALL of your histamine enzymes.
Histamine doesn’t just live in your gut. It is body-wide.
DAO is one of many enzymes that works to break down and clear histamine from your body. By supporting ALL of your histamine enzymes, many people are able to finally achieve relief.†*
4.
Test Your Histamine Genes.
Did you know that you can TEST for mutations (AKA polymorphisms) in your histamine enzymes?
The StrateGene® Report shows you (on a visual map) if any of your histamine metabolism genes/enzymes have mutations. This is critical information, because targeted supplementation can act as a ‘work-around’ for common histamine gene mutations.
The StrateGene® Report doesn’t just show you where your Histamine Genes (and over 100 other genes!) need support, it tells you what nutrients you need, which ones to avoid, lifestyle habits to follow, and so much more!
References
- 1 Is there a diet for histamine intolerance? - pubmed.gov
- 2 Highlights in cardiovascular effects of histamine and H1-receptor antagonists - pubmed.gov
- 3 Biogenic Amine - sciencedirect.com
- 4 Diamine oxidase supplementation improves symptoms in patients with histamine intolerance - pubmed.gov
- 5 Histamine and histamine intolerance - pubmed.gov
- 6 Histamine Intolerance: The Current State of the Art - PubMed Central
- 7 HNMT Gene - Histamine N-Methyltransferase - genecards.org
- 8 Histamine N-methyltransferase regulates aggression and the sleep-wake cycle - nature.com
- 9 Impaired resolution of wheals in the skin prick test and low diamine oxidase blood level in allergic patients - PubMed Central
- 10 Impaired resolution of wheals in the skin prick test and low diamine oxidase blood level in allergic patients - PubMed Central






